Women’s Power in America
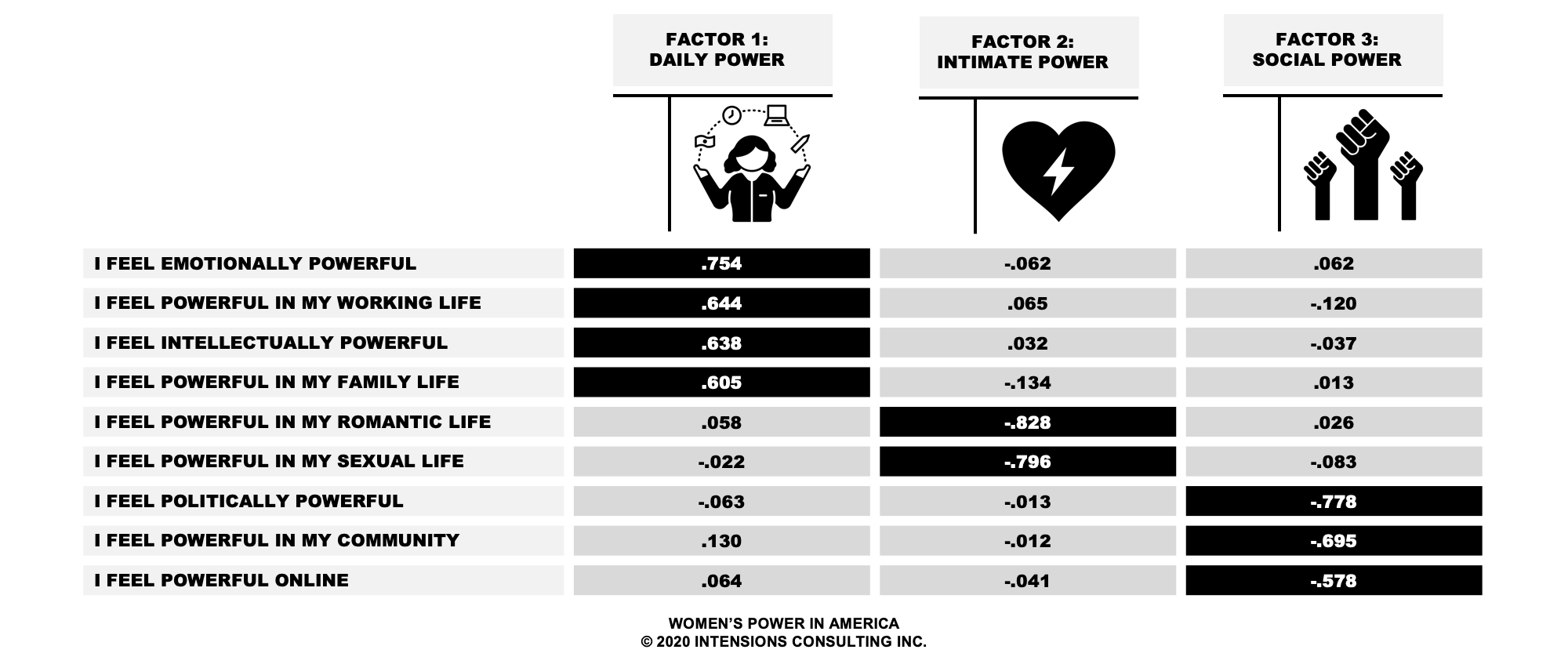
This research explored the feelings of power experienced by 4,010 American women, between the ages of 16 and 44 years. Using market segmentation techniques called exploratory factor analysis and k-means clustering, we managed to identify three Women’s Power Factors: Daily Power, Intimate Power, and Social Power.
For this research respondents completed a self-report questionnaire on feelings of power, with each item rated on a 5-point agreement scale. Principal-axis factoring was conducted using a direct oblimin rotation (delta=0), as factors were expected to be correlated. Factors were extracted using parallel analysis, a highly accurate method for determining factors in principal-axis factoring (Velicer et al., 2000). Three factors were identified, accounting for 55.26% of the variance in the data. Internal consistency was acceptable to good for all three factors: Daily Power (α=.79), Intimate Power (α=.83), and Social Power (α=.77). Following principal-axis factoring, items from each factor were categorized into high and low groups using k-means clustering.
Factor 1: Women’s Daily Power
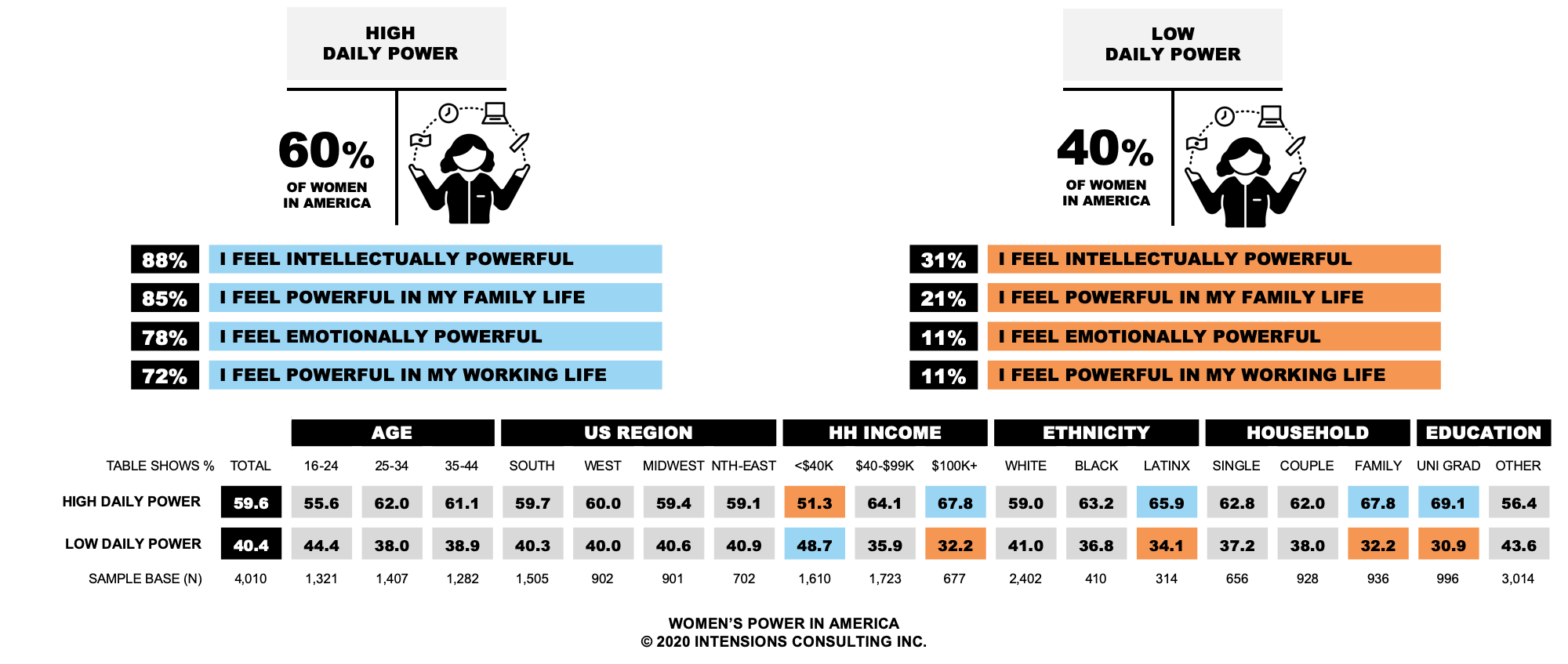
The first factor incorporates women’s feelings of power in their working life, family life, emotionally, and intellectually. Our research found that 60 per cent of American women could be classified as being High in Daily Power, and 40 per cent of American women could be classified as being Low in Daily Power.
From a demographic perspective, American women who are High in Daily Power are more likely to have a household income over 100,000 dollars, identify as Latinx, live with a partner and children, and have graduated university. Women who are Low in Daily Power are more likely to have a household income under 40,000 dollars.
Factor 2: Women’s Intimate Power
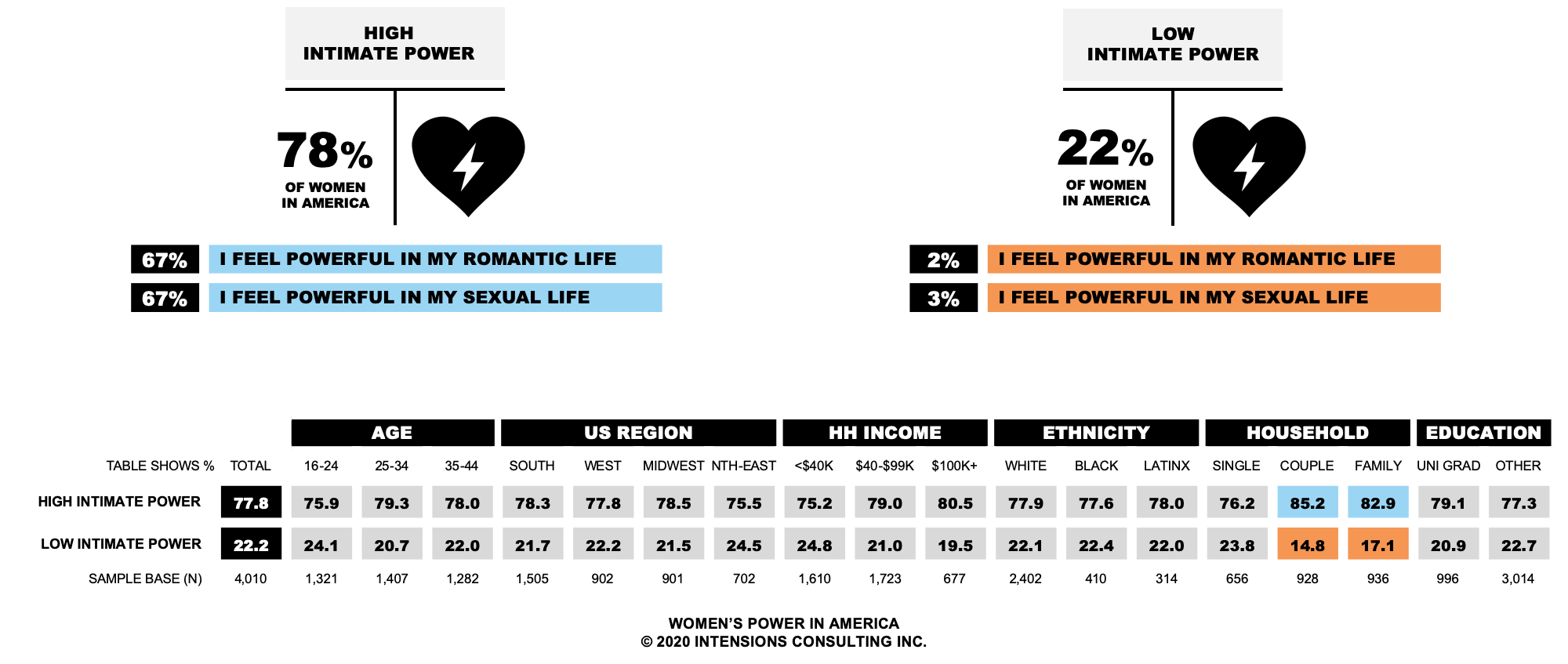
The second factor incorporates Americans women’s feelings of power in their romantic and sexual life. Our research found that 78 per cent American women could be classified as being High in Intimate Power, and 22 per cent of American women could be classified as being Low in Intimate Power.
From a demographic perspective, American women who are High in Intimate Power are more likely to live with a partner or live with a partner and children.
Factor 3: Women’s Social Power
This factor incorporates American women’s feelings of power politically, online, and in their community. Our research found that 61 per cent of American women could be classified as being High in Social Power, and 39 per cent of American women could be classified as being Low in Social Power.
From a demographic perspective, American women who are high in Social Power are more likely to identify as Black.
About This Research
These are findings from an Intensions Consulting study conducted between December 27, 2018, and January 6, 2019. For this study an online survey was administered with a sample of 4,010 American women, between the ages of 16 and 44 years. The sample was stratified to ensure that the sample’s composition reflected the underlying distribution of the population as determined by Census data. A traditional probability sample of comparable size would have produced results considered accurate to within plus or minus 1.5 percentage points, 19 times out of 20.
For more information on this research, please contact: info@intensions.co
References
- Velicer, W. F., Eaton, C. A., & Fava, J. L. (2000). Construct explication through factor or component analysis: A review and evaluation of alternative procedures for determining the number of factors or components. In R. D. Goffin & E. Helmes (Eds.), Problems and solutions in human assessment: Honoring Douglas N. Jackson at seventy (pp. 41-71). Norwell, MS: Kluwer. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4397-8_3